As seen previously, arguments are passed to a function by value. There is no direct way for the function to alter a variable in the calling function. Let’s look at the swap function:
void swap(int a, int b)
{
a = a + b;
b = a - b;
a = a - b;
}
As a and b are copies of the actual argument passed to swap, the function only affects the copies and doesn’t actually swap the original variables.
We could re-write swap using pointers to fix this:
void swap(int *px, int *py)
{
*px = *px + *py;
*py = *px - *py;
*px = *px - *py;
}
We could call this swap and pass the addresses of the variables to be swapped like this:
swap(&x, &y);
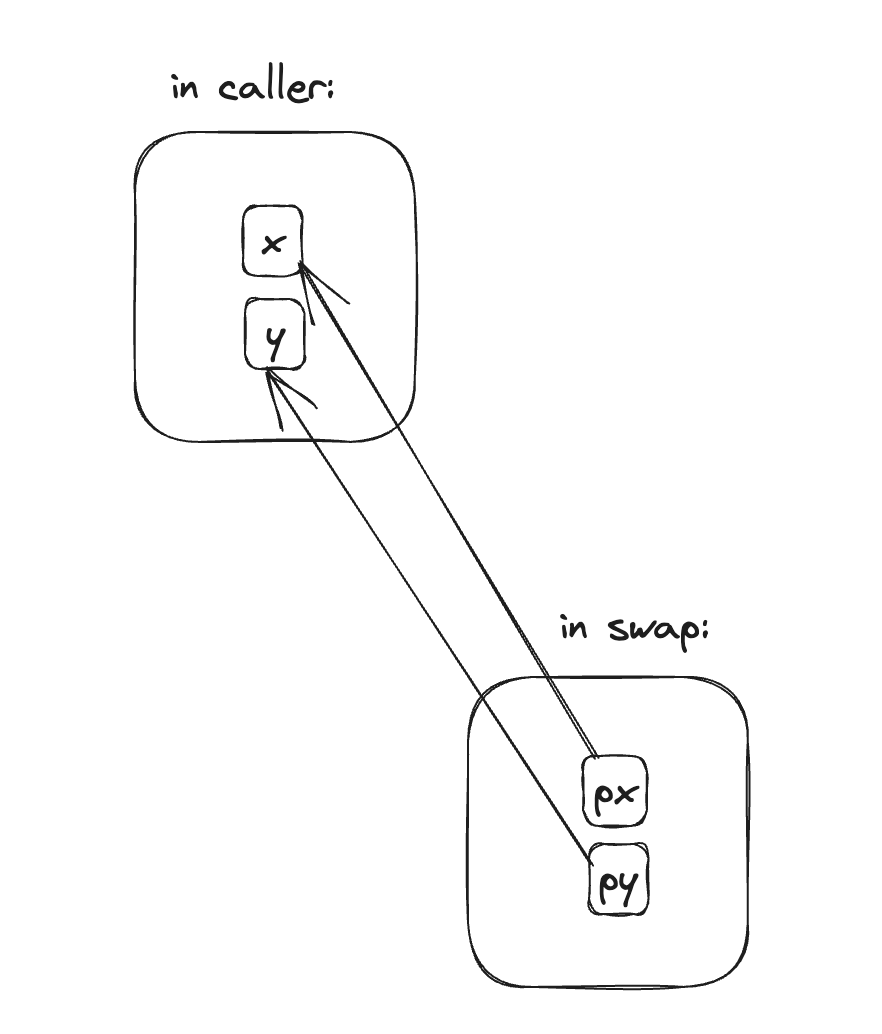
Pointer arguments enable a function to access and change objects in the function that called it.